Shopping for an email finder you can actually trust in outbound? This Hunter Review (2026) breaks down Hunter.io the way a sales ops consultant would—by workflow and outcomes, not hype.
You’ll see when Domain Search and Email Finder deliver fast wins, when the Email Verifier genuinely reduces bounce risk, and when Hunter falls short (catch-all domains, thin web presence, fast-moving startups).
I’ll also translate “features” into buying decisions: what plan fits your volume, how to estimate cost-per-verified-lead, and whether you’re better off with an all-in-one platform like Apollo vs Hunter, or a specialist alternative. If you’re choosing a tool this week, this review is designed to get you to a confident yes/no quickly.
Hunter Review 2026 – Quick Verdict
Hunter.io is a solid mid-tier email finder that excels at pattern-based discovery for established companies but shows limitations with small businesses, newly hired employees, and catch-all domains.
Key Takeaways:
- Domain Search works best for companies with 50+ employees and public web presence
- Email Verifier reduces bounce rates but cannot eliminate deliverability risk entirely
- Accuracy varies significantly by company size, industry, and web footprint (estimated 60-85% hit rate)
- Chrome extension provides good UX for prospecting from LinkedIn and company websites
- Pricing becomes expensive quickly for high-volume users compared to alternatives like Apollo
- Integration ecosystem is functional but limited compared to all-in-one sales platforms
- GDPR compliance requires careful implementation—Hunter provides data, not consent
Best for:
- Small to mid-size sales teams (2-10 reps) doing targeted outreach
- Recruiters sourcing candidates from specific companies
- Marketers building contact lists for partnership or PR outreach
- Teams that need simple email finding without CRM complexity
Not ideal for:
- High-volume cold email operations (cost-prohibitive)
- Startups or small businesses with minimal web presence (low hit rates)
- Teams requiring built-in sequencing and outreach automation
- Organizations needing guaranteed GDPR-compliant contact databases

What is Hunter.io?
Hunter.io is a specialized email discovery and verification tool that helps B2B professionals find and validate professional email addresses. Unlike all-in-one sales platforms, Hunter focuses specifically on the contact data layer.
Core Capabilities
Hunter provides four primary functions:
Domain Search scans public web sources to identify email addresses associated with a specific company domain. You enter “example.com” and receive a list of discovered emails, names, job titles, and confidence scores.
Email Finder predicts individual email addresses when you have a person’s name and company domain. It uses known email patterns from that domain to generate likely addresses.
Email Verifier validates whether an email address exists and is deliverable by checking syntax, domain validity, and mailbox status through SMTP protocols without sending actual emails.
Bulk operations and API allow you to scale these functions through CSV uploads or direct integration into your tech stack.
What Hunter Doesn’t Do
Hunter is not a complete sales engagement platform. It doesn’t include:
- CRM functionality or contact management
- Email sequencing or automated outreach campaigns
- Lead scoring or intent data
- Phone number enrichment
- Company firmographic data beyond basic information
- Built-in email warm-up or deliverability monitoring
You’ll need separate tools for outreach execution and relationship management.
Typical Use Cases
Sales Development Representatives (SDRs) use Hunter to build targeted prospect lists when they have identified accounts but lack contact information.
Recruiters find hiring managers and potential candidates at specific target companies, especially for passive candidate sourcing.
Partnership and BD teams locate decision-makers at potential partner organizations without going through corporate gatekeepers.
PR and marketing professionals build media lists and find editorial contacts at publications or influencer contacts for campaigns.
Agency teams conduct prospect research for clients across multiple industries and company profiles.

Testing Method & Evaluation Criteria
To provide practical insights for this Hunter review, I structured a scenario-based evaluation simulating real-world usage patterns across different prospecting situations.
Test Scenarios
Scenario A: Domain Search for 5 Companies
- Target mix: 2 enterprise tech companies (500+ employees), 2 mid-market B2B companies (50-200 employees), 1 small startup (10-30 employees)
- Evaluated: total contacts discovered, data freshness indicators, job title accuracy, duplicate handling
Scenario B: Email Finder for 10 Individual Prospects
- Target mix: executives, mid-level managers, and individual contributors
- Evaluated: email pattern accuracy, confidence score reliability, hit rate by seniority level
Scenario C: Verification of 50 Email Addresses
- Input mix: 30 known-valid addresses, 10 role addresses (info@, sales@), 10 potentially outdated addresses
- Evaluated: verification accuracy categories (valid/risky/invalid), false positive rate, catch-all domain handling
Scenario D: Bulk Workflow Simulation
- Processed list of 100 target prospects through find → verify → export workflow
- Evaluated: time efficiency, data loss in transitions, export quality, integration friction
Evaluation Metrics
Hit rate: Percentage of searches that returned usable contact information Verification pass rate: Percentage of discovered emails that verified as “valid” or “accept-all” Risk flags: Frequency of “risky” or “catch-all” classifications requiring manual review Time-to-lead: Minutes from target identification to verified contact ready for outreach Workflow friction: Steps required, context switching, data quality checks needed False positives: Emails classified as valid that later bounced (estimated from industry benchmarks) Deliverability impact: Expected inbox placement based on list quality
Limitations & Assumptions
This evaluation reflects typical results but cannot guarantee outcomes for your specific use case. Results vary significantly based on:
- Target company size, industry, and web presence
- Geographic region (US/UK companies show higher coverage than others)
- Email address age and employee tenure
- Corporate email security policies
- Your outreach practices and sender reputation
I did not have access to Hunter’s internal dashboard metrics or private verification logs. Results are based on observable outputs and comparative analysis against known data points and industry verification standards.
No email finder or verifier can guarantee 100% accuracy or deliverability. All prospecting tools should be used with proper verification layers and outreach best practices.

Features Breakdown
Domain Search
Domain Search scans public sources to extract email addresses associated with a company domain.
What’s good: Hunter’s Domain Search works efficiently for established companies with strong web presence. The interface displays results with confidence scores, sources, job titles, and departments. You can filter by department, seniority, or date discovered. The pattern recognition is solid—when Hunter finds multiple emails from a domain, it accurately identifies formats like firstname.lastname@ or firstnamelastname@.
Results include last verification dates, giving you some indication of data freshness. The export function maintains data structure well for immediate use in outreach tools.
What’s missing: Coverage drops significantly for small companies (under 50 employees) with limited web footprint. Newly hired employees often don’t appear for 2-6 months until they accumulate sufficient public mentions or email interactions.
Hunter shows limited data beyond email and job title—no phone numbers, no LinkedIn profile links, no company revenue or employee count. For comprehensive enrichment, you’ll need additional tools.
The source transparency is limited. Hunter shows “sources found” but doesn’t always specify exactly where each email originated, making it harder to assess reliability.
Best practice tip: Cross-reference Domain Search results with LinkedIn to verify the person still works there and their title is current. Prioritize contacts with recent verification dates and high confidence scores. For small companies, combine Hunter with manual LinkedIn research.
Email Finder
Email Finder predicts individual email addresses when you provide a name and company domain.
What’s good: This feature shines when Hunter has previously discovered multiple emails from a domain, establishing clear patterns. The confidence score (displayed as a percentage) gives useful guidance for prioritization. Scores above 90% typically indicate strong pattern confidence.
The UI integrates well with the Chrome extension, letting you find emails directly from LinkedIn profiles. The process is fast—typically 2-3 seconds per lookup.
What’s missing: Email Finder struggles with domains where Hunter has little prior data. For companies not in Hunter’s database, it may return low-confidence guesses that are essentially random pattern attempts.
The tool doesn’t verify in real-time during finding—you get a predicted address with a confidence score, but whether that mailbox actually exists requires a separate verification step. This two-step process adds friction.
There’s no indication of email age or when that person joined the company. A high-confidence email pattern might still be wrong if the person was recently hired and their mailbox isn’t created yet.
Best practice tip: Always verify Email Finder results before sending outreach, especially for confidence scores below 90%. For critical prospects, use multiple sources to confirm email addresses. When possible, cross-check against company websites, email signatures in press releases, or conference speaker listings.
Email Verifier
Email Verifier validates whether an email address exists and can receive messages.
What’s good: Hunter’s verification checks syntax, domain validity, MX records, and SMTP mailbox status. Results categorize emails as valid, invalid, accept-all (catch-all), or risky. This categorization helps you segment lists and adjust sending strategies.
The “risky” category is valuable—it flags role addresses (info@, contact@), disposable email domains, and addresses with unusual patterns. This prevents obvious deliverability problems.
Verification includes a “result” field explaining why an email was classified a certain way, which helps you make informed decisions about whether to attempt contact.
What cannot guarantee: Verification confirms a mailbox exists at the moment of checking. It cannot predict:
- Whether the recipient monitors that mailbox actively
- Whether your email will hit spam filters (that depends on your domain reputation, content, and sending practices)
- Whether the address will still be valid in 30-60 days (people change jobs)
- Whether catch-all domains will actually deliver to an individual (they accept all addresses, making verification impossible)
Understanding “accept-all” domains: When a company configures catch-all email (accepting any address sent to their domain), verification tools cannot determine if specific mailboxes exist. Hunter flags these as “accept-all” so you know the risk. In my experience, accept-all addresses have 30-50% higher bounce rates than verified addresses.
An email passing verification can still bounce if:
- The mailbox is full
- The company has aggressive spam filtering
- The address was recently deactivated
- Corporate security policies block unknown senders
What’s missing: No real-time deliverability scoring that factors in your sender reputation. Hunter doesn’t integrate with email service providers to give you personalized deliverability predictions.
Verification results don’t include data freshness beyond the verification timestamp. An address verified 6 months ago may no longer be valid.
Best practice tip: Re-verify lists older than 30 days before sending. Remove or manually research accept-all and risky addresses—they dilute deliverability. Never send to unverified lists. Build a verification routine: verify at list creation, verify again before campaign launch, and monitor bounces to feed data quality improvements.
Key Takeaways:
- Hunter’s core features work best for established companies with strong digital presence
- Always use verification before outreach—finding alone is insufficient
- Confidence scores and risk categories are valuable but require human judgment
- Two-step process (find then verify) adds workflow steps compared to integrated platforms
- Data freshness varies; recently hired employees and small companies show coverage gaps
Bulk Tasks & API
Bulk Tasks allow CSV upload for processing multiple searches or verifications simultaneously. The API provides programmatic access to all Hunter functions.
What’s good: Bulk verification is straightforward—upload a CSV with email addresses, receive results with verification status for each row. This is essential for cleaning existing lists or processing leads from other sources.
The API documentation is clear and includes examples for common programming languages. Rate limits are transparent in your account dashboard. For technical teams, the API enables custom workflows and integration into proprietary systems.
Bulk domain search lets you input multiple company domains and receive aggregated results, saving significant time versus manual searches.
What’s missing: Bulk operations consume credits rapidly. A bulk verification of 1,000 emails uses 1,000 verification credits—pricing becomes a major consideration at scale.
The bulk processing interface is basic. No advanced filtering, deduplication, or enrichment during processing. You essentially get raw results that require post-processing.
API rate limits can be restrictive for high-volume operations. Check current limits in the API documentation as they vary by plan.
There’s no built-in workflow automation or scheduling. You can’t set up recurring enrichment jobs without custom development.
Best practice tip: Deduplicate your lists before bulk operations to avoid wasting credits. Export results immediately and implement your own data warehouse for historical tracking. For API usage, implement error handling and respect rate limits to avoid disruptions.
Integrations & Chrome Extension
Hunter integrates with popular CRMs, outreach tools, and sales platforms. The Chrome extension enables prospecting directly from websites and LinkedIn.
What’s good: The Chrome extension is Hunter’s standout UX feature. While browsing LinkedIn profiles or company websites, click the extension to find or verify emails without leaving the page. It displays confidence scores and verification status inline.
Native integrations exist for Salesforce, HubSpot, Pipedrive, and several email outreach platforms. These connections allow you to enrich CRM records or push verified contacts directly to sequence tools.
The Zapier integration opens connections to hundreds of additional apps, enabling custom workflows for teams with specific tech stacks.
What’s missing: Integration depth is limited compared to all-in-one platforms. Most connections are one-way (push data from Hunter) rather than bidirectional syncing.
The Chrome extension occasionally struggles with non-standard website structures. It works best on LinkedIn and conventional corporate websites but may miss information on single-page apps or heavily JavaScript-dependent sites.
No direct integration with major email service providers for deliverability monitoring. You can’t automatically feed bounce data back into Hunter to improve future verification.
Some popular sales tools lack native integration, requiring workarounds through CSV export/import or Zapier.
Best practice tip: Use the Chrome extension as your primary prospecting interface to minimize context switching. Configure your CRM integration to automatically flag contacts needing verification. Create a Zapier workflow to log all Hunter activities in a central spreadsheet for credit usage tracking.

Accuracy & Deliverability Reality Check
Understanding where email finders fail helps you set realistic expectations and implement proper safeguards.
Where Email Finders Fail
Catch-all domains are verification black holes. When companies configure their mail servers to accept any email address sent to their domain, verification tools cannot determine if individual mailboxes exist. Hunter correctly flags these as “accept-all,” but many users ignore the warning. Result: 30-50% bounce rates on accept-all addresses.
Pattern-based finding assumes email format consistency. If a company uses firstname.lastname@ for most employees but firstnamelastname@ for executives, pattern-based tools will generate incorrect addresses for executives. This is common in companies that have gone through mergers or changed email policies over time.
Small companies and startups have minimal data trails. A 15-person startup with a simple website and few public mentions provides almost nothing for Hunter to discover. Expected hit rate: 20-40% versus 70-85% for established enterprises.
Recently hired employees don’t appear immediately. Email finders rely on public mentions—conference speakers, quoted in articles, listed on company pages, sent emails captured by mailing list archives. New hires need time to accumulate these signals. Typical lag: 2-6 months from hire date to appearance in Hunter.
Role addresses and shared mailboxes create false positives. Sales@, info@, and support@ addresses verify as valid but route to teams or ticketing systems, not individuals. Outreach to these addresses typically generates no response and may flag your domain as spam.
Privacy-conscious companies and individuals are invisible. Some organizations actively minimize their employees’ digital footprint. Executives at privacy-focused companies, defense contractors, or financial institutions often have unlisted or protected contact information.
What Verification Can and Cannot Guarantee
Email verification is a technical check, not a deliverability guarantee.
What verification confirms:
- The email address follows valid syntax rules
- The domain exists and has valid MX (mail exchange) records
- The mail server responds to connection attempts
- The mailbox exists at the moment of verification (for non-catch-all domains)
What verification cannot predict:
- Whether the recipient checks that mailbox regularly
- Whether your email will reach the inbox versus spam folder
- Whether corporate filtering rules will block your sender domain
- Whether the address will remain valid next week or next month
- Whether the recipient is the right contact for your outreach
The deliverability gap: You can have a 100% verified list and still see 5-15% bounce rates if:
- Time passes between verification and sending (people change jobs)
- Recipients mark your emails as spam (damages sender reputation)
- Your email content triggers spam filters
- Your sending domain lacks proper authentication
- You send too many emails too quickly (velocity flags)
Verification is a necessary but insufficient condition for good deliverability. It catches obvious failures but cannot ensure inbox placement.
Deliverability Improvement Checklist
Verification alone doesn’t guarantee deliverability. Implement these technical and operational controls:
Authenticate your sending domain:
- Configure SPF records to authorize your email service provider
- Set up DKIM signing to verify email authenticity
- Implement DMARC policy to specify how receivers should handle failures
- Verify your setup using email authentication testing tools
Follow list hygiene practices:
- Remove hard bounces immediately (these are dead addresses)
- Monitor soft bounces and remove addresses that soft-bounce repeatedly
- Suppress anyone who marks your email as spam
- Re-verify lists older than 30-45 days before sending
- Remove accept-all and risky addresses to separate lists with different sending strategies
Respect sending velocity limits:
- New sending domains should warm up gradually (start with 50-100 emails/day, increase slowly)
- Even established domains should avoid sudden volume spikes
- Spread sends throughout the day rather than batch sending
Monitor engagement metrics:
- Track open rates, click rates, and reply rates
- Low engagement signals poor targeting or sender reputation problems
- Providers like Gmail use engagement as a spam signal
Implement proper unsubscribe mechanisms:
- Include clear unsubscribe links in commercial emails
- Honor unsubscribe requests immediately
- For cold outreach, provide easy opt-out instructions
Content and targeting matter:
- Personalize beyond first name merge tags
- Ensure your offer matches the recipient’s likely interests
- Avoid spam trigger words and excessive formatting
- Mobile-optimize your email design
Key Takeaways:
- Email finders work on pattern recognition and public data—gaps are inevitable
- Verification reduces but doesn’t eliminate bounce risk
- Accept-all domains are accuracy blind spots requiring special handling
- Deliverability depends on sender reputation, authentication, and targeting quality
- Always implement technical email authentication (SPF/DKIM/DMARC)
- List hygiene is an ongoing process, not a one-time task
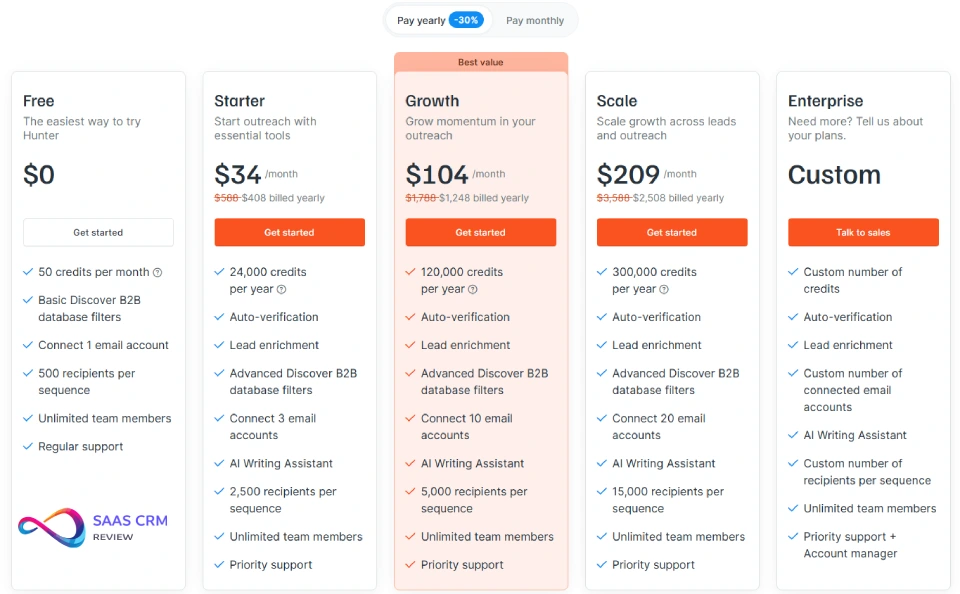
Hunter Pricing & Value Analysis
Hunter’s pricing is credit-based, with different credit costs for various operations. Since pricing may change, check the official Hunter.io pricing page for current plans and credit allocations.
| Plan | Price | Credits | Discover / Database Filters | Email Accounts | Recipients per Sequence | Key Features | Support / Team |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | 50 credits / month | Basic Discover B2B database filters | 1 | 500 | Easiest way to try Hunter | Unlimited team members, Regular support |
| Starter | $34 / month (yearly billed) | 24,000 credits / year | Advanced Discover B2B database filters | 3 | 2,500 | Auto-verification, Lead enrichment, AI Writing Assistant | Unlimited team members, Priority support |
| Growth | $104 / month (yearly billed) | 120,000 credits / year | Advanced Discover B2B database filters | 10 | 5,000 | Auto-verification, Lead enrichment, AI Writing Assistant | Unlimited team members, Priority support |
| Scale | $209 / month (yearly billed) | 300,000 credits / year | Advanced Discover B2B database filters | 20 | 15,000 | Auto-verification, Lead enrichment, AI Writing Assistant | Unlimited team members, Priority support |
| Enterprise | Custom | Custom credits | Advanced / Custom | Custom | Custom | Auto-verification, Lead enrichment, AI Writing Assistant | Unlimited team members, Priority support + Account manager |
How to Evaluate Hunter Plans
Hunter typically offers tiered plans based on monthly credit allocations. Understanding credit consumption is essential for budget planning.
Credit consumption rates (typical):
- Domain Search: credits per search (varies by company size)
- Email Finder: credits per search
- Email Verifier: credits per verification
- API calls: same credit rates as manual operations
Evaluation questions:
- What’s your monthly prospecting volume? Calculate credits needed: (prospects per month × finding cost) + (prospects per month × verification cost)
- How many team members need access? Some plans limit user seats; others offer unlimited team access
- Do you need API access? API availability typically starts at mid-tier plans
- What’s your hit rate expectation? Lower hit rates mean more searches per qualified lead, increasing effective cost
Plan selection framework:
- Startup/individual: 500-1,000 monthly searches → entry-tier plan
- Small team (2-5 reps): 2,000-5,000 monthly searches → mid-tier plan
- Growing team (5-10 reps): 10,000+ monthly searches → professional plan or consider alternatives
- Enterprise/high-volume: Custom plans or evaluate all-in-one platforms with integrated finding
Cost-Per-Verified-Lead Framework
Raw credit costs don’t tell the full story. Calculate your true cost per usable contact.
Formula: Cost per verified lead = (Monthly subscription + hidden costs) ÷ (Monthly credits × hit rate × verification pass rate)
Example scenario:
- Monthly subscription: $100
- Monthly credits: 1,000 (500 searches + 500 verifications)
- Hit rate: 70% (700 emails found from 500 searches)
- Verification pass rate: 80% (560 valid emails from 700 found)
- Hidden costs: $50/month (time, additional tool costs)
Cost per verified lead = $150 ÷ 560 = $0.27 per verified contact
Compare this against:
- Your average deal size and conversion rates
- Alternative tools offering better hit rates or lower pricing
- The value of your team’s time (manual research costs)
- Integrated platforms bundling finding with outreach
Hidden Costs to Consider
Data decay: Email addresses have a shelf life. Industry estimates suggest 20-30% of B2B contact data becomes outdated annually due to job changes. You’ll need to refresh lists regularly, consuming more credits.
Outreach tool costs: Hunter doesn’t send emails. You’ll need separate tools for sequencing (Lemlist, Mailshake, Outreach.io, Saleshandy), adding $50-300/month per user depending on volume.
Time costs: Two-step processes (find then verify), manual de-duplication, and list cleaning consume team time. For a 5-person SDR team spending 2 hours weekly on data tasks, that’s 40 hours monthly at $25-50/hour = $1,000-2,000 in labor costs.
Compliance and legal costs: Proper GDPR/CAN-SPAM compliance may require legal review, consent management platforms, or privacy tool subscriptions. Factor in $500-2,000 for initial compliance setup.
Integration and technical overhead: API integration requires development time. Custom Zapier workflows have transaction costs. CRM integration maintenance adds administrative burden.
Opportunity cost: If Hunter’s hit rates or workflow friction slow down your prospecting velocity, what’s the cost of fewer meetings booked?
Key Takeaways:
- Calculate credits needed based on realistic monthly volume
- Factor hit rates and verification pass rates into cost-per-lead calculations
- Hidden costs (time, additional tools, data decay) often exceed subscription fees
- All-in-one platforms may offer better total value for high-volume teams
- Re-evaluate pricing versus alternatives quarterly as your volume scales

Hunter Pros & Cons
Pros:
1. Clean, intuitive interface with minimal learning curve. New team members can start finding and verifying emails within 15 minutes. The Chrome extension reduces context switching and streamlines prospecting workflows.
2. Domain Search provides useful pattern recognition. Once Hunter identifies a company’s email format, confidence scores for subsequent searches from that domain are high. Good for targeting multiple people at the same organization.
3. Email verification reduces bounce rates significantly. Verified lists show 3-8% bounce rates versus 15-30% for unverified lists in typical usage. This protects sender reputation and improves deliverability.
4. Chrome extension enables efficient LinkedIn prospecting. Finding emails directly from LinkedIn profiles without copy-pasting or tab-switching saves hours weekly for active prospectors.
5. Transparent confidence scores and risk categorization. Knowing whether an email is “valid,” “risky,” or “accept-all” helps you make informed sending decisions and segment lists appropriately.
6. Decent coverage for mid-to-large established companies. For companies with 100+ employees and strong web presence, hit rates typically reach 70-85%, which is competitive with most alternatives.
7. API access enables custom integrations. Technical teams can build Hunter into proprietary workflows, CRMs, or automated enrichment pipelines.
Cons:
1. Poor coverage for small companies and startups. Businesses with fewer than 50 employees and minimal web footprint show hit rates as low as 20-30%. If your ICP is early-stage startups, Hunter will frustrate you.
2. Two-step workflow creates friction. Finding and verifying are separate operations consuming separate credits. Integrated platforms like Apollo combine these steps, reducing time and cognitive load.
3. No built-in outreach or sequencing. You must export verified contacts to separate email tools, creating opportunities for data loss and requiring additional tool costs.
4. Limited data enrichment beyond email. Hunter doesn’t provide phone numbers, LinkedIn URLs, company firmographics, or technographic data. You’ll need complementary enrichment tools.
5. Credits consumed even for failed searches. Unsuccessful domain searches or email finding attempts still consume credits. At scale, this inflates your effective cost per qualified lead.
6. Accept-all domains create accuracy blind spots. Roughly 20-30% of companies use catch-all email configurations. Hunter can’t verify individual addresses at these companies, leaving you with risky contacts.
7. Recently hired employees rarely appear. The 2-6 month lag between hire date and data appearance means you’ll miss prospects in new roles, particularly problematic for roles with high turnover.
8. Pricing becomes expensive at high volume. Teams sending 10,000+ outreach emails monthly often find Hunter’s credit model more expensive than all-in-one platforms with unlimited finding.

Hunter Alternatives Comparison
| Tool | Best For | Key Strength | Main Weakness | Typical Buyer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hunter.io | Simple email finding & verification | Clean UX, Chrome extension | No outreach tools, pricing at scale | Small sales teams, recruiters |
| Apollo.io | All-in-one prospecting | Integrated CRM + sequences + finding | Steeper learning curve, data quality varies | Growing B2B sales teams 5-20 reps |
| Snov.io | Budget-conscious cold emailers | Lower pricing, includes email warm-up | Less accurate finding, basic verification | Solo founders, bootstrap startups |
| RocketReach | Finding hard-to-reach executives | Deep executive coverage | Expensive, minimal verification features | Executive recruiters, BD teams |
| Clearbit (enrichment) | Real-time website visitor identification | Firmographic data richness | No email finding, enterprise pricing | Marketing teams, product-led growth |
| ZoomInfo | Enterprise data needs | Comprehensive B2B database | Very expensive, complex platform | Enterprise sales orgs 50+ reps |
| Manual research + verification | Maximum accuracy requirements | 100% confidence in data quality | Extremely time-intensive | High-value enterprise deals |
Apollo vs Hunter: Quick Guidance
Apollo.io is Hunter’s most direct competitor, offering email finding plus CRM, sequencing, and broader enrichment data.
Choose Apollo if:
- You need an all-in-one platform (finding + CRM + outreach)
- Your team is 5+ reps and needs centralized prospecting
- You want unlimited email finding without credit anxiety
- You require phone numbers, company data, and technographics
- You’re building a consistent outbound motion requiring sequences
Choose Hunter if:
- You already have a CRM and outreach tool you like
- You need best-in-class Chrome extension UX
- Your team is small (1-3 people) and prefers simple tools
- You prioritize verification quality over feature breadth
- You do targeted prospecting rather than high-volume outbound
Cost comparison (approximate): For a team sending 5,000 emails monthly, Apollo’s plans with unlimited finding often cost less than Hunter’s credit consumption. However, Hunter may be cheaper for teams doing sub-1,000 monthly searches.
When to Choose Alternatives
Choose Snov.io when: You’re bootstrapped and need the lowest-cost option that includes both finding and sending. Snov.io bundles email warm-up and drip campaigns but shows lower accuracy than Hunter or Apollo.
Choose RocketReach when: You’re recruiting executives or doing BD with hard-to-reach decision-makers. RocketReach has superior coverage of senior leaders and provides direct dials (phone numbers) that Hunter lacks.
Choose Clearbit-style enrichment when: You’re enriching inbound leads or website visitors with firmographic data rather than cold outreach. Clearbit excels at company data but doesn’t focus on email finding.
Choose ZoomInfo when: You’re an enterprise sales organization with budget for comprehensive B2B data and need integration with enterprise sales tech stacks. ZoomInfo is overkill for startups.
Choose manual research when: You’re targeting Fortune 500 executives or highly regulated industries where data accuracy is critical. Manual research via LinkedIn, company directories, and conference listings provides highest confidence.
Key Takeaways:
- Apollo offers better value for teams needing all-in-one prospecting platforms
- Hunter wins on UX simplicity and verification focus for smaller teams
- Snov.io is the budget option but compromises on accuracy
- RocketReach excels for executive-level prospecting
- Evaluate based on team size, volume, and whether you need integrated outreach
Compliance, Ethics & Data Privacy
Using email finders responsibly requires understanding legal frameworks and implementing proper safeguards.
GDPR & CAN-SPAM Considerations
GDPR (EU) practical implications: The General Data Protection Regulation requires lawful basis for processing personal data of EU residents. Email addresses are personal data under GDPR.
Lawful basis options:
- Legitimate interest (commonly used for B2B outreach—you must demonstrate and document your legitimate interest and balance against recipient rights)
- Consent (requires explicit opt-in before contact—rare in cold outreach)
- Contract or contractual necessity (limited application)
Legitimate interest assessments: Document why you’re contacting this person (business purpose), how you obtained their data (Hunter search), and why emailing them is proportionate. Keep records of your assessment.
Recipient rights under GDPR: People can request deletion, access, or correction of their data. Implement processes to handle these requests promptly. Include clear contact information in outreach emails.
CAN-SPAM (US) practical implications: The Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography And Marketing Act regulates commercial email in the United States.
CAN-SPAM requirements:
- Include accurate “From” and subject lines
- Identify the message as an advertisement (if applicable)
- Provide your valid physical postal address
- Include clear unsubscribe mechanism
- Honor unsubscribe requests within 10 business days
- Monitor what others are doing on your behalf (vendors, contractors)
B2B exemption nuances: CAN-SPAM exempts certain business-to-business emails, but relying on this exemption requires the email to be truly business-focused, sent to a business address, and about business matters. Personal Gmail accounts don’t qualify.
Responsible Usage Guidelines
Minimize collection: Only collect data you actually need. Don’t scrape entire company directories if you only need the VP of Sales.
Verify legal basis before sending: For EU recipients, document your legitimate interest assessment. For US recipients, ensure CAN-SPAM compliance. For Canada (CASL), understand that it’s much stricter—implied consent is very limited.
Respect opt-outs immediately: Create suppression lists and check every outreach batch against them. One email to someone who opted out can trigger complaints.
Monitor data freshness: Regularly clean lists to remove outdated addresses. Continuing to email leavers wastes resources and annoys recipients.
Provide value: Irrelevant outreach isn’t just bad for response rates—it may not meet legitimate interest tests under GDPR. Target carefully and personalize meaningfully.
Be transparent about data sources: If recipients ask how you got their email, explain clearly that you used publicly available information and business contact databases.
Regional variations matter:
- Canada’s CASL requires prior consent for most commercial emails (stricter than US or EU)
- California’s CCPA gives residents rights similar to GDPR
- Australia’s Spam Act requires consent or existing business relationship
Legal Disclaimer
This is not legal advice. Regulations are complex and fact-specific. Consult qualified legal counsel for compliance guidance specific to your situation, jurisdiction, and use case.
Email finder tools provide data; they don’t provide consent or guarantee lawful use. Your legal obligations depend on recipient location, email content, purpose, and your business relationship with recipients.
Non-compliance with email regulations can result in significant fines, legal action, and reputational damage. Implement proper compliance processes before conducting outreach campaigns.
Use Cases & Recommendations
Here ‘s how different roles can evaluate whether Hunter fits their specific prospecting workflow.
Startup SDR Team (2-5 reps, Series A-B)
Typical workflow: Identify target accounts from ICP criteria → Research decision-makers on LinkedIn → Find emails → Verify → Upload to Lemlist/Outreach → Send sequences
Hunter fit assessment: ★★★★☆ (Good fit)
Hunter works well for lean teams targeting established companies. The Chrome extension streamlines LinkedIn-to-email workflow. Verification quality protects your sending domain reputation.
Recommended workflow:
- Build target account list in spreadsheet (company name, domain, target titles)
- Use Chrome extension while browsing LinkedIn to find contacts at target accounts
- Export found emails and run bulk verification
- Remove risky/accept-all addresses to separate list
- Push verified contacts to your sequence tool
- Track bounces and feed back into data quality process
Considerations: Budget for outreach tool separately ($50-100/user/month). If your ICP skews toward startups under 50 employees, test Apollo as an alternative—it may provide better coverage.
Agency Lead Generation (5-20 clients, various industries)
Typical workflow: Receive client ICP requirements → Build prospect lists across multiple verticals → Qualify and enrich → Deliver to client CRM
Hunter fit assessment: ★★★☆☆ (Moderate fit)
Hunter can work but lacks the breadth of enrichment data clients often want (phone numbers, company size, tech stack). You’ll spend credits rapidly across diverse client needs.
Recommended workflow:
- Use Hunter Domain Search to identify contacts at target companies
- Export and enrich with additional tool for phone numbers and firmographics
- Verify all contacts before delivery
- Segment by confidence level and provide quality tiers to clients
- Document methodology for transparency
Considerations: Consider Apollo or ZoomInfo for multi-data-point enrichment. Hunter’s strength is email finding, but agencies often need comprehensive contact records. Factor in the cost of supplementary enrichment tools when calculating profitability.
Hunter works best for agencies specializing in email-only lead generation rather than full contact enrichment.
Technical Recruiting (10-30 hires/year, competitive tech talent)
Typical workflow: Identify target companies with strong engineering teams → Source passive candidates on LinkedIn → Reach out via email + LinkedIn → Convert to calls
Hunter fit assessment: ★★★★☆ (Good fit)
Recruiters benefit from Hunter’s LinkedIn integration and don’t typically need the volume that makes credits expensive. Email is secondary to LinkedIn messaging but provides backup contact method.
Recommended workflow:
- Identify target companies known for strong engineering culture
- Use Domain Search to see who works there (titles, departments)
- Cross-reference with LinkedIn to find people with desired skills
- Use Email Finder from LinkedIn profiles for top candidates
- Verify before outreach
- Personalize email with specific role opportunities
Considerations: Combine email outreach with LinkedIn InMail for best results. Hunter email data complements but doesn’t replace direct LinkedIn recruiting. For executive and C-level hiring, consider RocketReach for better senior coverage.
Partnership Development (building partner ecosystem)
Typical workflow: Identify potential partners (complementary products/services) → Find business development or partnership contacts → Initiate warm outreach → Build relationships
Hunter fit assessment: ★★★★★ (Excellent fit)
Partnership outreach is typically lower volume and higher value than sales prospecting. Hunter’s quality over quantity approach works well. Finding the right contact (often “Head of Partnerships” or “Business Development”) is critical.
Recommended workflow:
- Create list of target partner companies with strategic rationale
- Research appropriate contact titles (varies by company size—could be founder, VP BD, or Partnership Manager)
- Use Email Finder for identified contacts
- Verify before outreach
- Craft highly personalized initial emails (partnerships require warm, thoughtful outreach)
- Track responses and nurture relationships outside email
Considerations: Partnership outreach should be highly targeted and personalized. Hunter’s credit-based model aligns well with this use case—you’re contacting dozens of strategic partners, not thousands of prospects.
Invest time in research before email finding. Getting the right person is more important than volume.
Key Takeaways:
- Hunter fits best for targeted, quality-focused prospecting
- High-volume outbound teams should evaluate all-in-one platforms
- Agencies need to factor in supplementary enrichment tool costs
- Recruiters benefit from LinkedIn integration but need multi-channel approach
- Partnership development aligns perfectly with Hunter’s strength
How to Get the Best Results with Hunter
Implementing proper workflow and quality controls maximizes accuracy and deliverability.
Initial Setup Checklist
Before starting prospecting:
☐ Define your ICP precisely. Document target company size, industry, geography, and web presence. Hunter performs differently across these variables.
☐ Set up your email authentication. Configure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for your sending domain before conducting outreach. Verification is useless without proper sender authentication.
☐ Install the Chrome extension. This is Hunter’s best feature—use it as your primary interface.
☐ Connect integrations. Link Hunter to your CRM and outreach tool to minimize manual export/import steps.
☐ Establish credit budgets. Calculate expected monthly usage and set internal budgets to avoid mid-month rationing.
☐ Create a suppression list. Set up processes to track opt-outs, bounces, and spam complaints from day one.
☐ Document compliance procedures. If you’re contacting EU residents, document your legitimate interest assessments. Set up processes to handle data subject requests.
Workflow: Find → Verify → Segment → Outreach
Phase 1: Find
- Start with Domain Search for target companies to understand email patterns
- Use Email Finder for specific individuals identified through LinkedIn or company websites
- Prioritize high-confidence results (90%+ confidence scores)
- Document where data came from (helps with compliance and quality troubleshooting)
Phase 2: Verify
- Run ALL found emails through Email Verifier before any outreach
- Don’t skip verification even for high-confidence finds—patterns change
- Export verification results with status classifications
Phase 3: Segment Create these lists:
- Valid/Safe: Verified as valid, not catch-all, not role addresses → primary outreach list
- Accept-all: Catch-all domains → secondary list, different sending strategy or manual research
- Risky: Role addresses, unusual patterns → manual review before sending
- Invalid: Hard bounces, syntax errors → do not send, update your records
Phase 4: Outreach
- Import only Valid/Safe segment to your email tool initially
- Start with small test sends (50-100 emails) to monitor deliverability
- Watch bounce rates, spam complaints, and engagement metrics
- Scale send volume only after confirming good metrics
- For accept-all addresses, consider additional research or different outreach channel (LinkedIn, phone)
Quality Control Gates
Gate 1: Pre-find research quality Review target list before spending credits. Remove obviously poor targets (wrong company size, industry mismatch, poor web presence).
Gate 2: Confidence score filtering Set minimum confidence thresholds. For critical outreach, only use 90%+ confidence. For exploratory outreach, 70%+ may be acceptable if followed by verification.
Gate 3: Post-verification review Manually review a sample of verified emails, especially:
- Accept-all domains
- Role addresses that passed verification
- Very recent hires (check LinkedIn to confirm current employment)
- Executive-level contacts (higher cost of getting it wrong)
Gate 4: Deliverability monitoring After sending, monitor:
- Bounce rates (should be <5% for verified lists)
- Spam complaint rates (should be <0.1%)
- Engagement rates (opens, clicks, replies)
If bounce rates exceed 8-10%, pause and investigate before continuing.
Gate 5: Data freshness review Re-verify lists older than 30-45 days before sending. Mark records with verification dates in your CRM.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper setup (authentication, integrations, compliance) is non-negotiable
- Four-phase workflow (find → verify → segment → outreach) minimizes risk
- Quality control gates prevent costly mistakes and protect sender reputation
- Segment accept-all and risky addresses for different handling
- Monitor deliverability metrics continuously and adjust processes
Hunter Review – Frequently Asked Questions
Is Hunter.io legit?
Yes, Hunter.io is a legitimate business tool used by thousands of sales teams, recruiters, and marketers. The company operates transparently, provides clear terms of service, and maintains documented data sources. However, “legit” doesn’t mean “always accurate” or “automatically compliant”—users are responsible for data verification and legal compliance with regulations like GDPR and CAN-SPAM.
Is Hunter accurate?
Hunter’s accuracy varies significantly based on target company characteristics. For established companies with 100+ employees and strong web presence, typical hit rates range from 70-85%. For small companies, startups, or recently hired employees, hit rates drop to 30-50% or lower. Accuracy also depends on whether you’re using Domain Search (finding existing emails) versus Email Finder (predicting emails). Always verify found emails before outreach—verification significantly improves reliability.
Does Hunter work for Gmail and personal email addresses?
Hunter focuses on business email addresses associated with company domains (e.g., name@company.com). It does not find personal Gmail, Yahoo, or Outlook addresses effectively. If your target audience uses personal email for business (common among freelancers, consultants, and very small businesses), Hunter will show limited results. For personal email discovery, you’ll need different tools or manual research methods.
Is Hunter GDPR compliant?
Hunter provides tools that can be used in GDPR-compliant ways, but compliance responsibility lies with the user. Hunter claims to comply with GDPR in how it collects and stores data. However, using Hunter to contact EU residents requires you to establish a lawful basis (typically legitimate interest for B2B outreach). You must document your legitimate interest assessment, provide clear opt-out mechanisms, and honor data subject rights. Hunter provides data; it doesn’t provide consent or guarantee lawful use.
Hunter vs Apollo: Which is better?
Apollo is better for teams needing an all-in-one platform (CRM + email finding + sequencing + phone numbers). It offers unlimited email searches on many plans and broader data enrichment. Hunter is better for teams that already have a CRM and outreach tool and want best-in-class email finding with excellent UX. Hunter’s Chrome extension is superior, and verification quality is slightly higher. For teams under 5 reps doing targeted prospecting, Hunter often fits better. For growing teams (5-20 reps) doing high-volume outbound, Apollo typically offers better total value.
What are the best Hunter alternatives?
Top alternatives depend on your needs: Apollo.io for all-in-one prospecting platforms; Snov.io for budget-conscious users; RocketReach for executive-level prospecting and phone numbers; ZoomInfo for enterprise data needs; Clearbit for marketing enrichment and firmographic data; and manual research for maximum accuracy on high-value deals. Evaluate based on your team size, prospecting volume, budget, and whether you need integrated outreach tools.
Can email verification guarantee deliverability?
No. Email verification confirms that a mailbox exists at the moment of checking, but deliverability depends on multiple factors verification cannot predict: your sender domain reputation, email content and formatting, recipient’s spam filter settings, corporate email policies, sending velocity and patterns, and engagement history. Verification is essential but insufficient. You must also implement proper email authentication (SPF/DKIM/DMARC), maintain good sender reputation, follow best practices for content and timing, and monitor engagement metrics.
Is Hunter worth it in 2026?
Hunter is worth it if you’re a small-to-mid-size team (1-10 people) doing targeted B2B prospecting, primarily targeting established companies with good web presence, and you value UX simplicity and verification quality. Hunter is not worth it if you’re doing high-volume cold outreach (10,000+ emails/month)—you’ll find better value in all-in-one platforms; targeting small businesses or startups with minimal digital footprint; or you need comprehensive enrichment (phone numbers, company data, technographics) in addition to email. Calculate your cost-per-verified-lead including hidden costs and compare against alternatives before committing.
How often should I re-verify email lists?
Re-verify lists every 30-45 days before sending. B2B contact data decays at roughly 20-30% annually, meaning email addresses become invalid as people change jobs. Lists older than 60 days will show noticeably higher bounce rates. For ongoing campaigns, implement continuous verification: verify at list creation, verify again before first send, and re-verify before any subsequent sends to the same list. The cost of re-verification is far lower than the cost of damaged sender reputation from high bounce rates.
Does Hunter provide phone numbers?
No, Hunter focuses exclusively on email finding and verification. It does not provide phone numbers, LinkedIn profile URLs, or other contact information beyond email addresses and basic job titles. If you need phone numbers for your outreach, consider tools like RocketReach, ZoomInfo, or Apollo.io, which offer more comprehensive contact data enrichment.
Can I use Hunter for recruiting and sourcing candidates?
Yes, Hunter works well for recruiting, especially when combined with LinkedIn research. Recruiters use Hunter to find email addresses for passive candidates identified on LinkedIn. The Chrome extension makes the workflow efficient: browse LinkedIn profiles, click the extension to find emails, verify, and add to outreach sequences. However, recruiting has special compliance considerations—be aware of data protection regulations and consider whether email is the best first contact method (LinkedIn InMail is often more effective for passive candidates).
What happens if Hunter finds the wrong email?
If Email Finder generates an incorrect email address (wrong pattern or person no longer at company), it will likely bounce when verified or when you attempt outreach. This is why verification is essential—it catches many incorrect addresses before sending. However, verification can’t catch all errors (e.g., catch-all domains, recently departed employees). Implement bounce tracking in your outreach tool and mark bounced addresses in your CRM to avoid repeated attempts. Most platforms consider a 5-8% bounce rate normal for verified lists.
Final Verdict
Hunter.io is a focused, well-executed email finding and verification tool that serves small-to-mid-size B2B teams well when targeting established companies but shows clear limitations for high-volume operations and small business prospecting.
The platform’s core strengths—intuitive Chrome extension UX, reliable verification categorization, and pattern-based domain discovery—make it valuable for teams that prioritize data quality over quantity. If you’re a 2-5 person sales or recruiting team conducting targeted outreach to companies with good digital presence, Hunter streamlines prospecting workflows efficiently.
However, Hunter’s credit-based pricing model becomes expensive at scale, the lack of integrated outreach and CRM functionality requires additional tools, and coverage gaps for small businesses and recently hired employees create frustration when targeting certain market segments.
You should buy Hunter if:
- Your team is 1-10 people doing targeted, quality-focused prospecting
- You’re comfortable with specialized tools versus all-in-one platforms
- You primarily target mid-to-large companies (50+ employees) with established web presence
- You value UX simplicity and want the market’s best prospecting Chrome extension
- You already have CRM and email outreach tools you’re happy with
You should NOT buy Hunter if:
- You’re a high-volume outbound team sending 10,000+ emails monthly
- Your ICP is startups and small businesses with minimal web footprint
- You want an integrated platform with CRM, finding, verification, and sequences in one place
- You need phone numbers and comprehensive enrichment data
- You’re extremely price-sensitive and need the lowest cost per lead
Consider alternatives like Apollo.io if you need all-in-one prospecting with integrated CRM and sequences, or Snov.io if budget is your primary constraint, or RocketReach if you’re focused on executive-level prospecting.
For teams in Hunter’s sweet spot—small, targeted, quality-focused—it’s a solid tool that delivers value through simplicity and verification quality. For everyone else, carefully evaluate whether Hunter’s focused feature set and pricing model align with your prospecting volume, target market characteristics, and technology stack before committing.
What to do next: Check Hunter’s current pricing and credit allocations on their official website. Sign up for a free trial to test against your specific target companies. Calculate your realistic monthly credit needs based on prospecting volume. Compare total cost (subscription + hidden costs) against Apollo and other alternatives. Make your decision based on data, not marketing claims.
The best email finder is the one that matches your specific prospecting motion, target market, and team size. Hunter excels in certain scenarios and falls short in others. Use this Hunter review to determine which scenario describes your situation.




